Tính toán thông minh trong kỹ thuật xây dựng
- Giới thiệu
Cùng với sự phát triển của khoa học máy tính, các phương pháp tính toán thông minh dựa trên mạng nơ-ron nhân tạo và máy học ngày càng được ứng dụng rộng rãi trong các lĩnh vực kỹ thuật, đặc biệt là kỹ thuật xây dựng. Nhiều bài toán trong kỹ thuật xây dựng vẫn chưa có giải pháp tối ưu bằng các phương pháp truyền thống như giải tích, thực nghiệm và số (phương pháp phần tử hữu hạn, phương pháp phần tử rời rạc,...). Một số bài toán điển hình bao gồm:
- Ước lượng sức chịu tải dọc trục cực hạn của móng cọc.
- Đánh giá ổn định của các bài toán địa kỹ thuật: thi công đường hầm, mái dốc, tường chắn đất, móng nông.
- Đánh giá cường độ chịu lực còn lại của kết cấu bê tông cốt thép chịu ăn mòn.
- Dự báo chiều cao sóng tác động đến công trình bờ biển.
- Phát triển phương pháp tối ưu hóa thiết kế bền vững kết cấu xây dựng và vật liệu xây dựng.
- Địa kỹ thuật và địa vật lý ngoài khơi.
- Xữ lý nền đất yếu.
Việc áp dụng các phương pháp tính toán thông minh có thể giúp thu hẹp những khoảng trống nghiên cứu hiện nay, đồng thời cung cấp giải pháp tối ưu cho thực tiễn kỹ thuật xây dựng tại Việt Nam.
- Tầm nhìn và sứ mệnh
SCCE hướng đến việc trở thành nhóm nghiên cứu mạnh trong lĩnh vực tính toán thông minh ứng dụng trong kỹ thuật xây dựng. Các hướng nghiên cứu của nhóm tuân theo hai tiêu chí chính:
- Tính mới khoa học và tác động công nghệ: Các nghiên cứu mang tính tiên phong, có tiềm năng ứng dụng thực tiễn cao.
- Ứng dụng thực tế: Các bài toán nghiên cứu xuất phát từ nhu cầu thực tiễn của ngành xây dựng và có khả năng ứng dụng vào thực tế.
Ngoài ra, SCCE cam kết xây dựng một môi trường nghiên cứu học thuật có tính liêm chính cao, trách nhiệm và hướng tới mục tiêu dài hạn là cầu nối giữa giới khoa học và doanh nghiệp để thúc đẩy chuyển giao công nghệ.
- Các hướng nghiên cứu chính
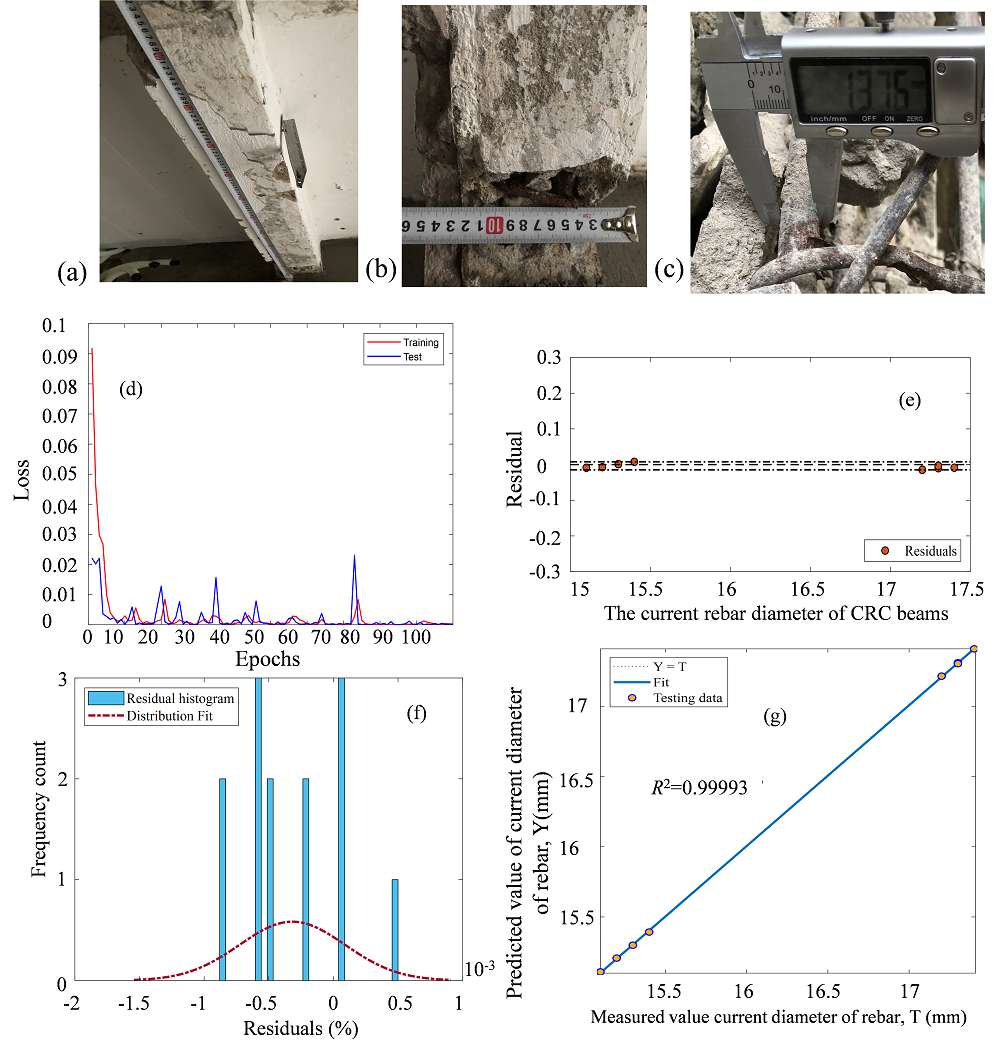
- Phát triển phương pháp tính toán thông minh kết hợp dữ liệu thực địa để giải quyết các bài toán cấp thiết như: (i) Sức chịu tải của móng cọc; (ii) Ảnh hưởng của ăn mòn cốt thép đến khả năng chịu lực của bê tông cốt thép;
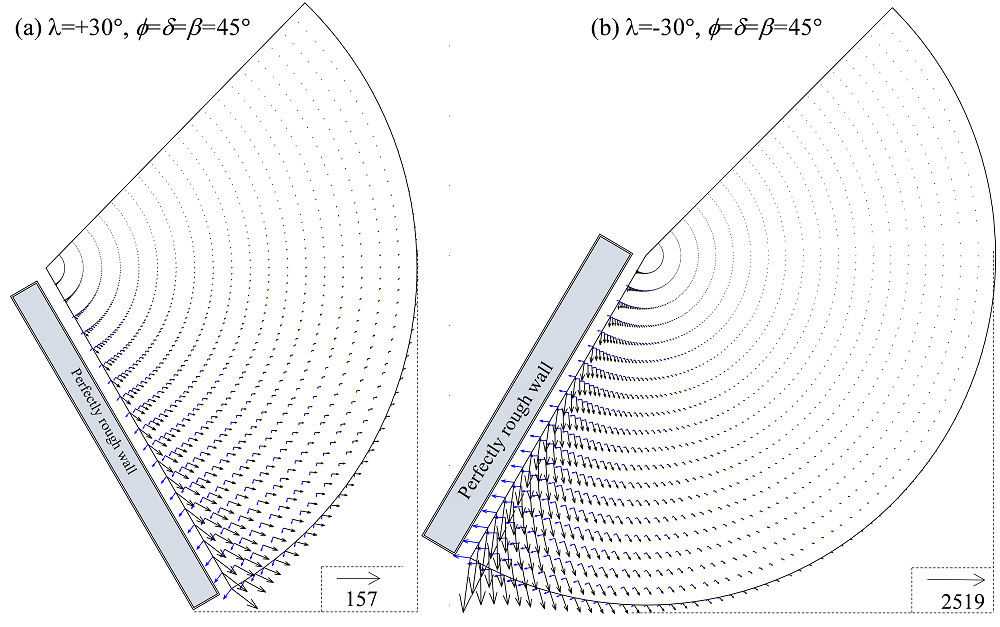
(2) Phát triển phương pháp số tích hợp bằng cách kết hợp trí tuệ nhân tạo với các phương pháp số truyền thống (phân tích giới hạn, phần tử hữu hạn, phân tích đẳng hình học) để giải quyết các bài toán địa kỹ thuật như ổn định mái dốc, sức chịu tải móng nông, thi công đường hầm.
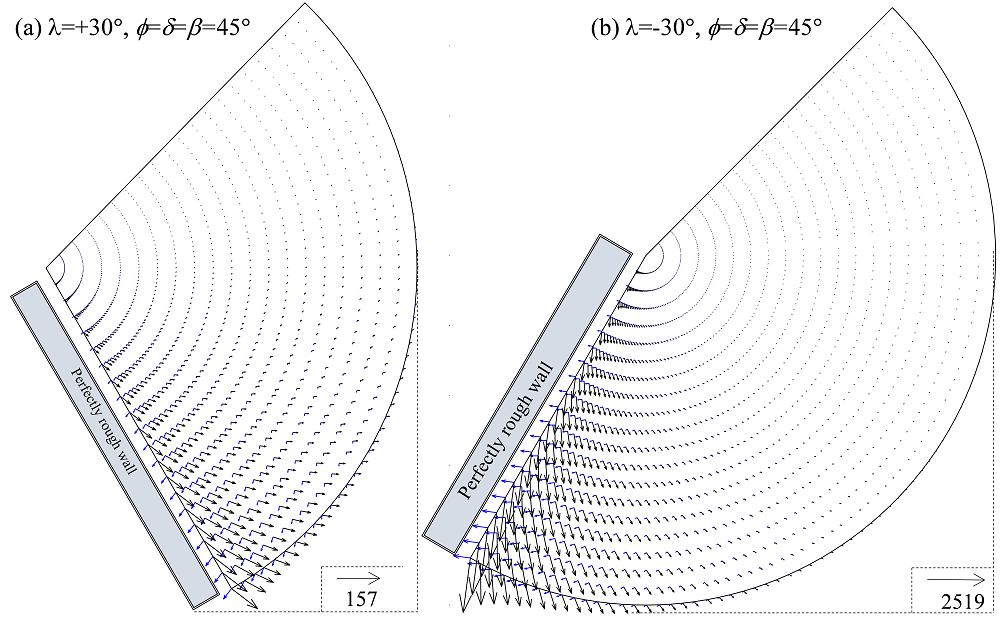
(3) Phát triển giải pháp chính xác cao bằng cách kết hợp các phương pháp số, giải tích và trí tuệ nhân tạo để giải quyết các bài toán trong địa kỹ thuật (áp lực đất lên tường chắn, ảnh hưởng của động đất lên công trình địa kỹ thuật) và kỹ thuật bờ biển (ước lượng chiều cao sóng, tiêu tán năng lượng sóng,...).
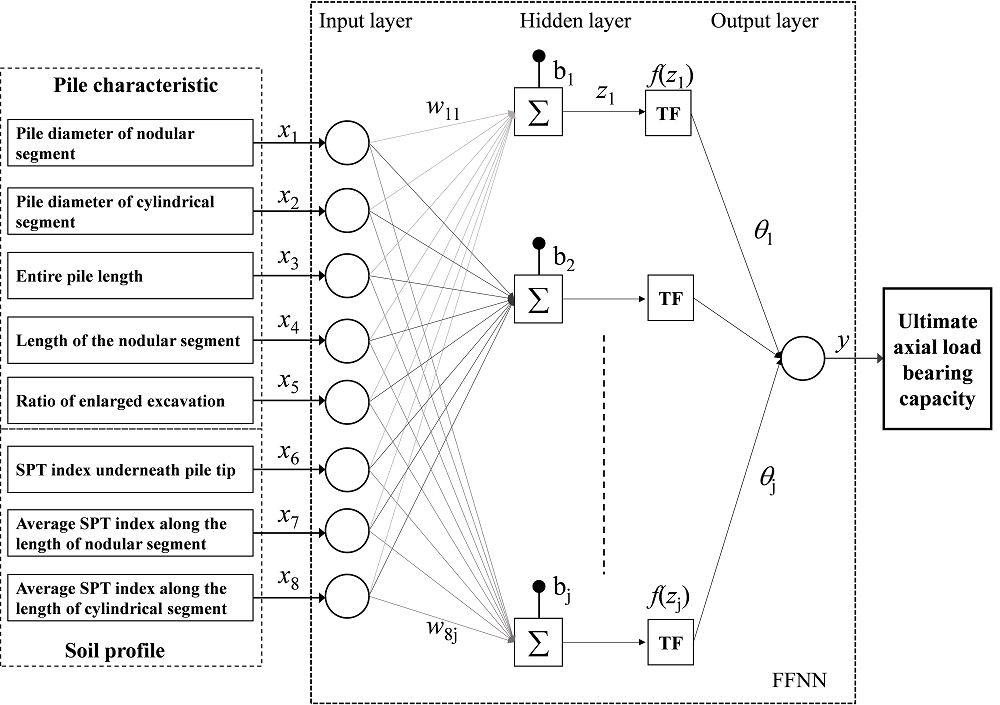
(4) Nghiên cứu cải thiện nền đất yếu.
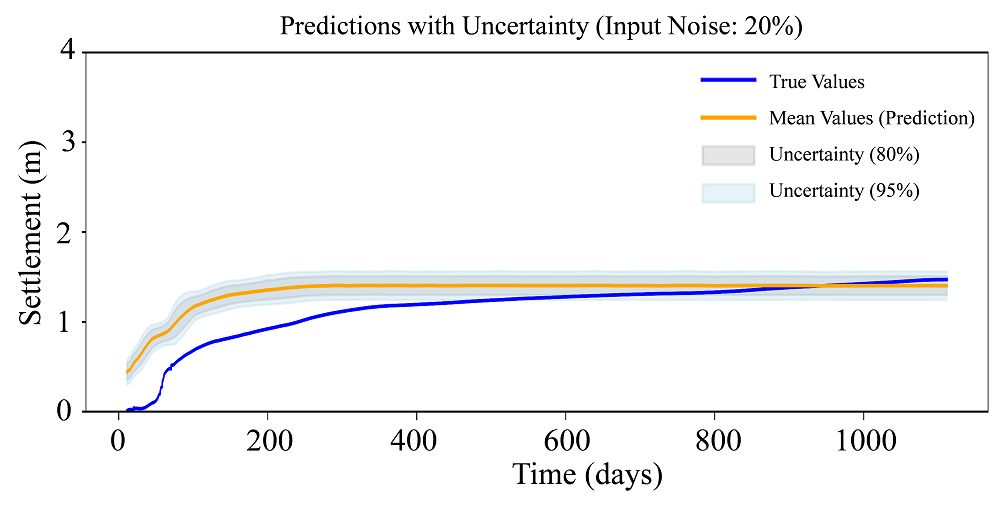
(5) Ứng dụng AI trong kỹ thuật nền móng ngoài khơi và địa vật lý biển.
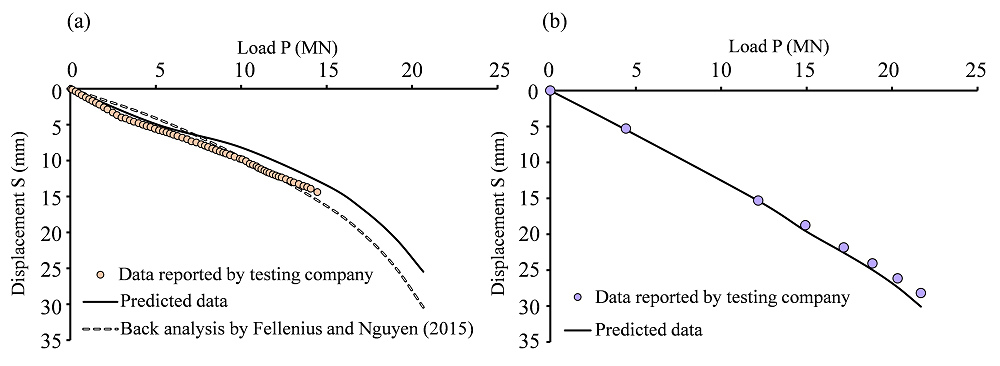
(6) Phát triển mô hình tính toán sóng biển dựa trên trí tuệ nhân tạo và thuật toán di truyền để dự đoán chiều cao sóng vỡ, năng lượng tiêu tán và các tham số quan trọng khác.
(7) Phát triển mạng nơ-ron nhân tạo có thông tin vật lý (PINN).
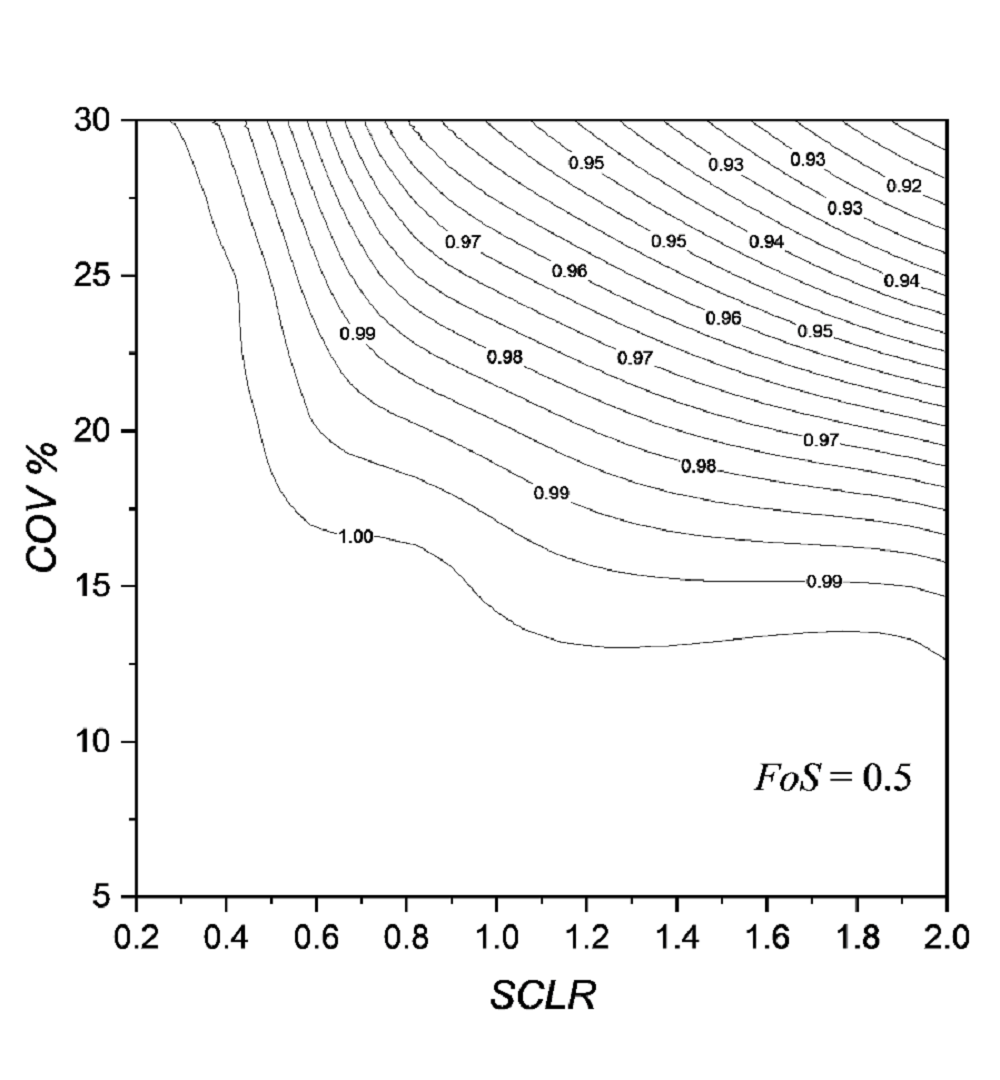
(8) Lý thuyết độ tin cậy trong phân tích các bài toán địa kỹ thuật
4. Nhân sự
|
|
TS. Nguyễn Tấn Vị trí: Trưởng nhóm Lĩnh vực nghiên cứu: Địa kỹ thuật, máy học, kết cấu bê tông cốt thép, cơ học đất tính toán, nền móng ngoài khơi, mạng nơ-ron nhân tạo có thông tin vật lý, kỹ thuật vật liệu xây dựng. Thành tích nghiên cứu: • Số lượng bài báo ISI đã công bố: 33 • Tổng số trích dẫn: 250 • ISI H-index: 10 |
|
|
TS. Trần Quang Khiêm Vị trí: Thành viên Lĩnh vực nghiên cứu: Kỹ thuật bờ biển, sự lan truyền sóng biển, xữ lý nền đất yếu, mạng trí tuệ nhân tạo, giải thuật biểu hiện gen.
|
|
|
|
5. Liên hệ
Nguyễn Tấn
Email: nguyentan@tdtu.edu.vn (hoặc nguyen.tan.48c@kyoto-u.jp)
Số điện thoại: (+84) 968.720.722
6. Các bài báo đã công bố
- Trần Quang Khiêm
[1] Duong, N.T., Tran, K.Q., Satomi, T. and Takahashi, H., 2022. Effects of agricultural by-product on mechanical properties of cemented waste soil. Journal of Cleaner Production, 365, p.132814.
[2] Duong, N.T. and Tran, K.Q., 2023. Estimation of seepage velocity and piping resistance of fiber-reinforced soil by using artificial neural network-based approach. Neural Computing and Applications, 35(3), pp.2443-2455.
[3] Tran, K.Q., Satomi, T. and Takahashi, H., 2019. Tensile behaviors of natural fiber and cement reinforced soil subjected to direct tensile test. Journal of Building Engineering, 24, p.100748.
[4] Tran, K.Q., Satomi, T. and Takahashi, H., 2018. Effect of waste cornsilk fiber reinforcement on mechanical properties of soft soils. Transportation Geotechnics, 16, pp.76-84.
[5] Tran, K.Q., Satomi, T. and Takahashi, H., 2018. Improvement of mechanical behavior of cemented soil reinforced with waste cornsilk fibers. Construction and Building Materials, 178, pp.204-210.
[6] Duong, N.T., Tran, K.Q., Luu, L.X. and Tran, L.H., 2023. Prediction of breaking wave height by using artificial neural network-based approach. Ocean Modelling, 182, p.102177.
[7] Rattanapitikon, W., Tran, K.Q. and Shibayama, T., 2015. Estimation of maximum possible wave heights in surf zone. Coastal Engineering Journal, 57(02), p.1550001.
[8] Tran, K.Q., Duong, N.T., Luu, L.X., Tran, L.H. and Rattanapitikon, W., 2023. Development of novel parametric wave model for irregular wave height transformation. Ocean Engineering, 278, p.114493.
[9] Tran, K.Q., Duong, N.T., Luu, L.X. and Tran, L.H., 2024. Unconfined compressive strength of geopolymers based soil: Model development using gene expression programming and a comparison with other computer-based approaches. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, pp.1-11.
- Nguyễn Tấn
[1] Nguyen, T., Pipatpongsa, T., Kitaoka, T. and Ohtsu, H., 2019. Stress distribution in conical sand heaps at incipient failure under active and passive conditions. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 168, pp.1-12.
[2] Wanjala, S.C., Pipatpongsa, T. and Nguyen, T., 2020. Experimental realization of incipient active failure in sand heap by seismic loading. Granular Matter, 22, pp.1-16.
[3] Nguyen, T. and Pipatpongsa, T., 2020. Plastic behaviors of asymmetric prismatic sand heaps on the verge of failure. Mechanics of Materials, 151, p.103624.
[4] Nguyen, T. and Tran, L.V., 2021. Arching effect in sand piles under base deflection using geometrically non-linear isogeometric analysis. Geomechanics and Engineering, 26(4), pp.369-384.
[5] Huynh, V.H., Nguyen, T., Nguyen, D.P., Nguyen, T.S. and Nguyen, T.C., 2022. A novel direct SPT method to accurately estimate ultimate axial bearing capacity of bored PHC nodular piles with 81 case studies in Vietnam. Soils and Foundations, 62(4), p.101163.
[6] Nguyen, T., 2022. Passive earth pressures with sloping backfill based on a statically admissible stress field. Computers and Geotechnics, 149, p.104857.
[7] Nguyen, T., Ly, K.D., Nguyen-Thoi, T., Nguyen, B.P. and Doan, N.P., 2022. Prediction of axial load bearing capacity of PHC nodular pile using Bayesian regularization artificial neural network. Soils and Foundations, 62(5), p.101203.
[8] Nguyen, T., Truong, T.T., Nguyen-Thoi, T., Bui, L.V.H. and Nguyen, T.H., 2022, December. Evaluation of residual flexural strength of corroded reinforced concrete beams using convolutional long short-term memory neural networks. In Structures (Vol. 46, pp. 899-912). Elsevier.
[9] Nguyen, T., 2023. An exact solution of active earth pressures based on a statically admissible stress field. Computers and Geotechnics, 153, p.105066.
[10] Nguyen, T., 2023. Statically admissible stress fields in conical sand valleys and heaps: a validation of Haar–von Kármán hypothesis. International Journal of Geomechanics, 23(2), p.04022286.
[11] Nguyen, T.H., Nguyen, T., Truong, T.T., Doan, D.T.V. and Tran, D.H., 2023, May. Corrosion effect on bond behavior between rebar and concrete using Bayesian regularized feed-forward neural network. In Structures (Vol. 51, pp. 1525-1538). Elsevier.
[12] Nguyen, B.P., Nguyen, T.T., Nguyen, T. and Guo, W., 2023. Analytical model for consolidation and bearing capacity of soft soil stabilized by combined PVD-deep cement mixing columns. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 82(7), p.286.
[13] Nguyen-Minh, T., Bui-Ngoc, T., Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Nguyen-Thoi, T., 2023. Coupling isogeometric analysis with deep learning for stability evaluation of rectangular tunnels. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 140, p.105330.
[14] Nguyen, T., Ly, D.K., Huynh, T.Q. and Nguyen, T.T., 2023. Soft computing for determining base resistance of super-long piles in soft soil: A coupled SPBO-XGBoost approach. Computers and Geotechnics, 162, p.105707.
[15] Nguyen, T. and Shiau, J., 2023. Revisiting Active and Passive Earth Pressure Problems using Three Stability Factors. Computers and Geotechnics, 163, p.105759.
[16] Nguyen, T. and Fellenius, B.H., 2024. Bidirectional static loading tests on barrette piles. A case history from Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 61(5), pp.872-884.
[17] Nguyen-Minh, T., Bui-Ngoc, T., Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Nguyen-Thoi, T., 2024. Undrained sinkhole stability of circular cavity: A comprehensive approach based on isogeometric analysis coupled with machine learning. Acta Geotechnica, pp.1-23.
[18] Nguyen, T., Shiau, J. and Ly, D.K., 2024. Enhanced earth pressure determination with negative wall-soil friction using soft computing. Computers and Geotechnics, 167, p.106086.
[19] Nguyen, T. and Shiau, J., 2024. Passive earth pressure in sand on inclined walls with negative wall friction based on a statically admissible stress field. Acta Geotechnica, pp.1-25.
[20] Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Ly-Khuong, D., 2024. Unraveling seismic uplift behavior of plate anchors in frictional-cohesive soils: A comprehensive analysis through stability factors and machine learning. Ocean Engineering, 297, p.116987.
[22] Shiau, J., Nguyen, T., Sams, M. and Bhattacharya, P., 2024. Innovative numerical modeling for predicting soil relaxation in the design of twin circular culverts. Scientific Reports, 14(1), p.7689.
[22] Van Tran, M., Ly, D.K., Nguyen, T. and Tran, N., 2024. Robust prediction of workability properties for 3D printing with steel slag aggregate using bayesian regularization and evolution algorithm. Construction and Building Materials, 431, p.136470.
[23] Nguyen, T., Ly, D.K., Shiau, J. and Nguyen-Dinh, P., 2024. Optimizing load-displacement prediction for bored piles with the 3mSOS algorithm and neural networks. Ocean Engineering, 304, p.117758.
[24] Bui-Ngoc, T., Nguyen, T., Nguyen-Quang, M.T. and Shiau, J., 2024. Predicting load–displacement of driven PHC pipe piles using stacking ensemble with Pareto optimization. Engineering Structures, 316, p.118574.
[25] Nguyen-Minh, T., Bui-Ngoc, T., Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Nguyen-Thoi, T., 2024. Synergistic Integration of Isogeometric Analysis and Data-Driven Modeling for Enhanced Strip Footing Design on Two-Layered Clays: Advancing Geotechnical Engineering Practices. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, pp.1-23.
[26] Nguyen, T.H., Vuong, H.T., Shiau, J., Nguyen-Thoi, T., Nguyen, D.H. and Nguyen, T., 2024. Optimizing flexural strength of RC beams with recycled aggregates and CFRP using machine learning models. Scientific Reports, 14(1), p.28621.
[27] Nguyen-Minh, T., Bui-Ngoc, T., Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Nguyen-Thoi, T., 2024. Hybrid deep learning and isogeometric analysis for bearing capacity assessment of sand over clay. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering.
[28] Shiau, J., Nguyen, T., Pham-Tran-Hung, T. and Sugawara, J., 2025. Probabilistic assessment of passive earth pressures considering spatial variability of soil parameters and design factors. Scientific Reports, 15(1), p.4752.
[29] Nguyen, M.T., Bui, T.N., Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Nguyen, T.T., 2025. Stability of rectangular tunnels in cohesive-frictional soil under surcharge loading using isogeometric analysis and Bayesian neural networks. Advances in Engineering Software, 201, p.103861.
[30] Nguyen-Thai, V., Ly, D.K., Nguyen, T. and Nguyen-Thoi, T., 2024, September. An effective optimum design for passive viscous damping control using FVDs/VWDs in multi-story buildings. In Structures (Vol. 67, p. 107004). Elsevier.
[31] Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Bui-Ngoc, T., 2024. Passive earth pressure on vertical rigid walls with negative wall friction coupling statically admissible stress field and soft computing. Scientific Reports, 14(1), p.21322.
[32] Nguyen-Minh, T., Bui, T.N., Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Nguyen-Thoi, T., 2025. A novel closed-form solution for circular tunnels in cohesive-frictional soils using isogeometric analysis, upper bound limit analysis, and soft computing. Computers and Geotechnics, 180, p.107104.
[33] Shiau, J., Nguyen, T. and Bishal Chudal, 2025. Advanced 3D Finite Element Limit Analysis for Assessing Blowout Stability in Water Main Bursts. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (In press)
- Log in to post comments